
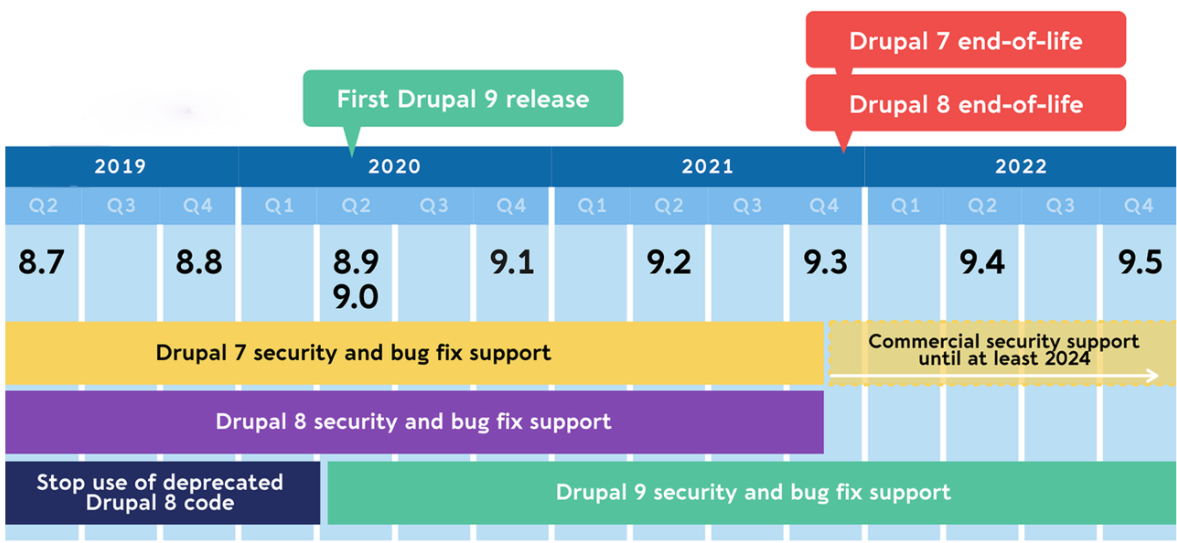
If you’re using Drupal 8, you may expect a similar experience when Drupal 9 comes out later this year in June. “The major deal with Drupal 9 is…that it shouldn’t be a huge issue,” Dries stated.
Drupal 9 will inherit all of the functionalities of Drupal 8 that have been updated and added by the Drupal community since 2015. For concrete confirming the platform security, a few modifications will be made, notably to system requirements and third-party dependencies that are as follows:
- It is mandatory with Drupal 9 to use the latest PHP and database versions.
- Where security support for dependent libraries is ending, these libraries have either been upgraded to newer versions like Symfony and Twig or replaced with best-in-class alternatives (in the case of many jQuery UI components).
Some of the Key Benefits of Drupal 9 Migration
- Drupal 9 delivers all of the features you enjoy from Drupal 8 to the next level, with widely compatible system requirements and components for better security.
- With feature improvements twice a year, Drupal 9 puts you on the cutting edge of technology. With new features, Drupal 9.1.0 was released on December 2, 2020.
- Drupal 9 will be extremely familiar to developers who have worked with Drupal 8. Thus, there will be no need for explicitly training the employees. Clean and consistent APIs create a contemporary environment for developers.
Source: Drupal.org
What You Need for Drupal 9 Migration
Your website is required to be updated with the newest minor version. Upgrades are only supported from the most recent planned minor release and one prior release (for example, Drupal 8.8 and 8.9), not from earlier versions like Drupal 8.3.
- Any obsolete modules on your site should be updated to the most recent versions. Drupal 9 may not comply with older module versions.
- Your hosting environment must fulfill the Drupal version you’re upgrading to its minimal system requirements (PHP 7.4 or later recommended).
Check your site for deprecated code that will be removed in the next major release. If necessary, fix any deprecations. Several modules may need to be upgraded. This is where the Upgrade Status module may help.
Four Steps to Prepare Drupal 8 Sites for 9 Migration
Here’s your to-do list for Drupal 9, the majority of which you can do with Upgrade Status:
- Verify that your hosting environment supports Drupal 9’s enhanced needs.
- Upgrades from Drupal 8.8 and 8.9 are supported. Update to the most recent Drupal 8 version.
- Maintain the status of your submitted projects. Most bestowed projects eventually tackle Drupal 9 compatibility concerns while maintaining Drupal 8 compatibility.
- Remove all references to deprecated APIs from your custom code. A large portion of these will be resolved automatically because of Rector.
You now have a fully functional Drupal 8 site that has been thoroughly cleansed. When all of your custom code and contributed projects are complete, you’re ready to upgrade Drupal core to Drupal 9.
System requirements
Specific hardware requirements must be met for the update to be successful. There are very likely needs for your system to function properly, which are as follows:
- If you’re running Drupal 9 on Nginx, you’ll need to update to version 0.7.x
- If you’re running Drupal 9 on Apache, you’ll need version 2.4.7
- Finally, you’ll need PHP version 7.3 to function with Drupal 9. You should also be aware that PHP 8 is supported by 9.1.0.
Database and Hosting Requirements
Because hosting requirements protect your online project, you must be certain of them, especially after a large upgrade. The four primary Drupal 9 hosts are given here and their prerequisites.
- If you’re using Drupal 9 with MySQL or Percona, you’ll need to upgrade to version 5.7.8 or higher.
- If you’re using Drupal 9 with Maria DB, you’ll need to upgrade to version 10.3.7+.
- Drupal 9 requires version 3.26 or above to work with SQLite.
- PostgreSQL version 10 and the pg_trgm extension are required when using Drupal 9 with PostgreSQL.
Source: Drupal.org
Here Is a Roadmap to Get You Started
➔ Create a Module Inventory
The Drupal 9 codebase is similar to Drupal 8.9, except it does not include the deprecated code. The impact of this deprecated code varies depending on what you’re using and which APIs you’ve used.
Custom modules, contrib modules, and themes are the three items to consider. Make a list in whatever format suits your group best.
Installing the Upgrade Status module is a good place to start. In a development environment, please enable it. This will offer you an excellent starting point for the data you wish to track. Install this patch for the module to obtain this data into a spreadsheet.
Because the Drupal development procedure for each category will change, organize the sheet so that you can filter your contrib and custom modules.
➔ Custom Modules
Install and execute drupal-check in your development environment or your continuous integration strategy. This will show you where you need to work to make your custom codebase Drupal 9 compliant.
The advantage of including it in your CI process is that it ensures that no new incompatibilities are introduced. There’s also a Visual Studio Code plugin.
Create a ticket in your ticketing system for each module with a Drupal 9 compatibility problem. Fill in the blanks. Minor adjustments, such as a different function call, will be required. Others may require more extensive reworking. Determine who they are as soon as feasible. Now is also a good time to look over the contrib area and determine whether you still require these custom modules.
➔ Themes
Keep note of any contrib base or sub-themes you use and treat them as modules by adding them to your list.
Moving from Twig 1 to Twig 2 has its own set of deprecations. Make sure your templates aren’t employing Twig methods that aren’t compatible with version 2. The Upgrade Status module should flag these. Many projects may not require any revisions, but it is essential to double-check early to avoid being caught off guard. Add any flags to your ticketing system as tickets.
Process For Migration to Drupal 9 From Drupal 8.7 or Earlier Versions
Drupal being the open-source platform, is freely available to create your website. It comes under the most famous CMS, which are built-in PHP languages. Professional web developers always recommend keeping the website updated with the latest Drupal versions to ensure data integrity and website operability. We have curated the following 13 steps, which you can follow for upgrading or migrating to Drupal version 9:
It is crucial to figure out the website scope, comprising the need for up-gradation for modules and themes. With “Upgrade Status,” a list can be generated to briefly plan and outline the website areas that need to be worked upon.
Install “Drupal-check” and “Upgrade Rector,” which will assist you in resolving problems persisting in website modules.
If any of the tools on your project break, you must build a temporary project using Drupal 8 and move the modules from your main website to the temporary project environment.
Step 2: Checking the host environment compatibility
Checking the host environment compatibility
Double-check your hosting environment to meet Drupal 9’s prerequisites & basic requirements. With the following reference list, you can check your environment compatibility too being with Drupal 9 upgradation:
Nginx:
- At least v 0.7.x is necessary if you’re running Drupal 9 on Nginx.
Apache:
- If you’re using Apache to run Drupal 9, you’ll need at least version 2.4.7.
PHP:
- Drupal 9 requires PHP 7.3 or higher. PHP 7.4 is also supported, however it isn’t mandatory. Drupal 9.1.0 is compatible with PHP 8.
Backend database:
- If you’re using Drupal 9 with MySQL or Percona, you’ll need version 5.7.8 or above.
- If you want to use Drupal 9 with MariaDB, you’ll need version 10.3.7 or above.
- If you’re using Drupal 9 with SQLite, you’ll need version 3.26 or above.
- If you’re using Drupal 9 with PostgreSQL, you’ll need version 10 of the pg_trgm extension.
[Note: For drush compatibility you can refer: Click here.]
Step 3: Verify that the website’s current version is 8.8.x or 8.9.x.
Make sure your website’s current version is 8.8.x or 8.9.x before updating the core to Drupal 9. If any of the tools on your project break, you must build a temporary project using Drupal 8 and move the modules from your main website to the temporary project environment.
Step 4: Scanning & Creating a list of all the libraries and themes used on the website.
List all of the libraries and themes installed on your website, including custom themes. It’s possible that some of the libraries and themes have updated their versions. Make a list of all the libraries and themes that need to be upgraded to the most recent version.
Step 5: Make a list of all the custom modules used on the website.
In an excel spreadsheet, make a list of all the contributed and custom modules that are installed on your website. The “Upgrade status” module can help you find the modules. This module looks over your site and tells you which modules are compatible with Drupal 9 and recommends that you upgrade them to the current version if any have been published.
Upgrade Status also recommends that you uninstall any deactivated modules. All of this information should be documented and kept up to date.
Step 6: Search your website for deprecated code.
When you use deprecated code, you will get warnings or problems. Use drupal-check to scan your website for obsolete code and generate a list of modules, themes, and libraries. If any of the functions you’re using have been deprecated, it will also propose a substitute.
List all of the problems that drupal-check has found in a document so that you may repair them more easily and in an efficiently planned manner.
Step 7: Double-check for library compatibility test.
Refer to the document you generated and update the libraries on your website to the most recent version that is Drupal 9 compliant. With the aid of the composer, you may update the libraries.
Step 8: Verify that modules are updated to the latest standards.
Update your website’s custom-created modules to Drupal 9’s most recent compatible version. Some of the deprecated problems found in step 6 may be automatically rectified after upgrading the modules, while others may persist.
If the issues persist after updating the module, and it is one of the custom modules, you may either discover and repair patches for those errors if one exists, or you can develop your own patch and contribute to the Drupal community.
If the problems are not causing any harm to your website, you can keep them until a new version of the module with the fixes corrected is published.
To apply a patch: Click Here To Visit Reference
Step 9: Double-check that custom modules are up to date.
Updating custom modules to make them Drupal 9 compliant necessitates manual code modifications. However, tools like “Upgrade Rector” can be utilized to give solutions for resolving faults discovered in step 6 or automate the correction of recognized mistakes.
Also, use drupal-check to see if any issues were missed by the “upgrade rector.”
Add a Drupal 9 compliant version of all custom modules after the issues have been addressed.
Example:
Step 10: Make sure all submitted themes are updated to their possible latest version.
Update any custom themes on your website to Drupal 9’s most recent version. Some of the deprecated mistakes may be immediately rectified when upgrading the themes, while others may persist.
You can apply the fixes to the remaining faults or keep them until a new version of the theme is published with the errors corrected.
Step 11: Check for your custom themes to be updated.
If your website uses custom themes, check that they don’t include any previous version code or mistakes that may prevent you from upgrading to Drupal 9.
With the aid of Drupal-check and upgrade rector, the issues may be resolved. Add a Drupal 9 compliant version of all custom themes after the issues have been corrected.
Step 12: Remove any modules that are no longer in use from the website.
Uninstall all of the unneeded modules that the upgrade status module recommended. You always have the option to leverage Drupal composer to remove the old modules.
Step 13: Upgrade to Drupal 9’s core codebase.
Finally, after the modules, themes, and libraries are Drupal 9 compliant, the Drupal core codebase may be upgraded to the stable version of Drupal 9.
Depending on whether your website uses “drupal/core” or “drupal/core-recommended,” you’ll need to update. “composer show drupal/core-recommended“ – This command will assist you in determining which package is being utilized.
The command will return detailed information about the package if “drupal/core-recommended” is installed; otherwise, it will produce a message saying “package drupal/core-recommended not found.”
If the project is using “drupal/core-recommended,” run the following command to upgrade the core codebase to Drupal 9’s newest stable version:
composer require ‘drupal/core-recommended:<version:name>’ — update-with-all-dependencies
If the project is utilizing “drupal/core,” run the following command to upgrade the core codebase to Drupal 9’s newest stable version:
composer require ‘drupal/core:<version:name>’ — update-with-dependencies
Following the successful upgrade of the Drupal core codebase, update the database to apply any needed upgrades.
Clear the cache and check the status report on the admin page: “Sitename/admin/reports/status” after the database has been refreshed.
The new version will be shown on the Status Report page.
Before attempting to update your site to Drupal 9, be sure that any custom code and/or themes are not utilizing any code that was deprecated in 8.8.x or earlier and will be removed in 9.0.x. Finally, upgrade the core codebase to Drupal 9 and execute update.php once every other component is Drupal 9 compatible.
Looking for Drupal Migration Services? Speak with our Drupal expert? – Don’t waste your time filling up the form, just call on +1 310-606-2426 and we are ready to discuss your project…
Girish Panchal
Technical ArchitectA Technical Architect, proficient in WordPress, Drupal, Laravel, and DevOps tasks, crafts robust IT solutions with a blend of expertise and versatility in web development and infrastructure management.











