
Google uses more than 200 ranking factors in their algorithm and the ranking algorithms are updated almost every day. Some of these changes are minor in nature whilst some updates may have a significant impact on SERP (Search Engine Results Pages).
In 2020, Google introduced three user-experience metrics – LCP, FID and CLS. These metrics will be known as Core Web Vitals and will be used in order to assess the overall experience of the users on a website. Core Web Vitals are going to have the final say with regards to a website’s Page Ranking.
New Ranking Factors Coming in 2021 – Core Web Vitals
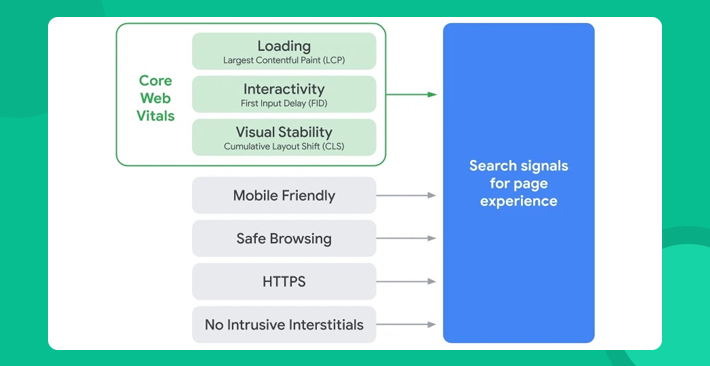
These new Core Web Vitals (user experience metrics) will not become a part of Google’s algorithm until 2021 (the exact date is yet to be released by Google). Some SEO experts have already started focusing on these changes in order to score perfect ranks, as these metrics define the user-experience needs that all types of websites are expected to fulfil according to Google. The Core Web Vitals are going to measure a website’s interactivity, visual stability and loading speed. These new signals will be used in 2021 along with other factors, such as mobile-friendliness, security, safety and number of pop-ups, when assessing the overall page experience.
The Old Page and New Page Experience
Google conducted extensive research over the years and tested the effectiveness of numerous metrics in measuring the users’ experience when interacting with a particular web page. Numerous metrics were primarily considered to be effective in measuring this factor during the research; however, most of them failed to generate the expected outcome. The Core Web Vitals are the chosen ones. Google finally found the metrics that satisfied all requirements.
According to Google, the Core Web Vitals will be able to measure the first impression of a user after visiting a web page. Google also claims that the websites capable of creating a positive first impression are 24% less likely to lose the users when a web page is loading. Therefore, Core Web Vitals are going to become important Page-ranking metrics.
The New Page Experience Ranking Factor
What is Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)?
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) is a user experience metric that evaluates the loading performance of a web page. This determines the load speed when the main content of the page has finished rendering on the screen.
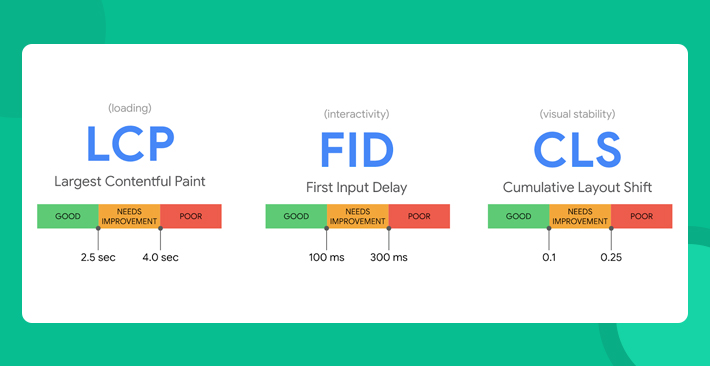
LCP is going to use the following benchmarks for user-experience.
- Good:
For web pages loading under 2.5 seconds - Need Improvement:
For web pages loading between 2.5-4 seconds - Poor:
For web pages taking more than 4 seconds to load
Google used the following metrics before LCP
- First Paint
- First Contentful Paint
- First Meaningful Paint
- Time to Interactive
- First CPU Idle
However, all these metrics had some limitations. LCP is believed to be the ultimate find. It may not be perfect. However, Google believes this is the best measurement to find out how fast does a web page feel.
The largest content element (video/image/text) that is present on the screen takes some time to render. Google times the duration of rendering in order to calculate LCP. Google will switch to the next largest element as a screen’s composition changes when it is loading. Google continues this action until a web page has been fully loaded or until a user interacts with a web page. To improve the LCP, a website needs to fulfil the following demands.
- Speedy server response times
- Speedy resource loading
- Enhanced client-side rendering
- Less render-blocking CSS/JavaScript
What is First Input Delay (FID)?
First Input Delay (FID) is a user experience metric that evaluates the responsiveness of a webpage and quantifies the experience that users feel while seeking to first have interaction with the webpage.
It will use the following UX benchmarks.
- Good – Less than 100 ms
- Needs Improvement – Between 100-300 ms
- Poor – More than 300 ms
It takes some time for a web page to react to a user’s first action (click/tap/keypress). This duration is known as the ‘First Input Delay’. FID is going to be measured in-field, as a user has to determine when to perform the first action in this scenario. FID is reported to substitute the Total Blocking Time (TBT).
TBT is the period between the first appearance of any content and the time when a web page become responsive. It may correlate with FID; however, TBT reports larger values. To optimize the FID, the focus is on faster web page loading by using less JavaScript or through code-splitting.
What is Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)?
Cumulative Layout Shift (or CLS) is a user experience metric that evaluates the visual stability of a web page. This quantifies how much visible content shifted in the viewport as well as the distance the elements impacted were shifted.
It uses the following benchmarks to determine the user-experience.
- Good – Less than 0.1
- Needs Improvement – Between 0.1 and 0.25
- Poor – More than 0.25
If the web content does not stop moving or shifting even when a web page has loaded completely, then it may create a layout shift that is also known as layout Jank or Content Jank. It may be distracting and annoying for a user. When calculating the CLS score, the share of a screen that unexpectedly shifted when a web page was loading is multiplied by the distance it travelled.
For CLS optimization, it is essential to include size attributes for the images/videos. It is equally important not to insert new content on top of existing content for improved CLS.
Tools for Testing Core Web Vitals

The following tools will be used in order to measure the Core Web Vitals. Some of these tools use field-data from real users and some tools simulate the user-behaviour within a lab set-up to measure the performance.
Page Speed Insights (PSI)
PSI measures the performance of a web page on two different interfaces – desktop and mobile devices. After the analysis, it suggests how to improve the performance of a particular web page. PageSpeed provides two types of data after the analysis – Lab data and Field data.
- Lab data is gathered in a controlled environment.
- Field data is also known as RUM (Real User Monitoring) data.
- It includes the performance data that is collected when a real web page is loading.
Chrome UX Report
Chrome UX Report measures the data collected from opted-in users in the field instead of measuring the data collected in a controlled environment. It measures various metrics such as FCP, DCL and FID. Chrome UX Report is a public dataset. It includes the data on real user-experience. It is possible to collect the qualitative dimensions of UX through Chrome UX Report dataset.
Web Vitals Extension
The Web Vitals are quality signals key. They are used to measure the ‘Core Web Vitals’ in order to provide instant feedback on layout shift metric, interactivity and loading speed. This extension is consistent with Chrome in how the aforementioned metrics are measured and reported to other tools of Google, such as Search Console or Chrome User Experience Report. It can capture LCP, CLS and FID. This extension has the following features.
- Ambient Badge.
- A feature that enables users to drill into individual metric values.
- HUD overlay
Lighthouse
Lighthouse is an automated and open-source tool. It can be used to improve the quality of any web page. It is possible to run this tool against any web page whether it is public or requires authentication. It can audit a website to check its performance, progressive web apps, accessibility, SEO and various other features. Lighthouse runs a sequence of audits against a web page when it is provided with a URL. A ‘Reference doc’ explains the importance of each audit and suggests on how to fix an issue.
Chrome DevTools
Chrome DevTools is a set of tools for web developers. They are built into the browser of Google Chrome. Web-developers may use these tools to quickly diagnose an issue or to edit a web page whilst running a computer program. It is possible to quickly develop a quality website using Chrome DevTools.
Search Console
Webmasters can use the Google Search Console to monitor and to manage the websites through an official portal. This portal is full of useful statistics. Search Console works as a communication channel for Google and provides a set of tools for daily management. It is possible to learn how well a website is showing up on the search results using a GSC account.
Conclusion
By acting upon these factors, you can significantly improve website ranking and strengthen your branding, customer retention and sales. So, what are you waiting for, be ready to set out for these new ranking update and for any assistance feel free to contact KrishaWeb’s expert SEO and UX Developer Teams.











